What is Ransomware?
Ransomware is a type of malware that prevents or limits users from accessing their system, either by locking the system’s screen or by locking the users’ files unless a ransom is paid. Ransomware can be classified on its following based on the attacker actions
- Encrypting Ransomware (ENCRYPTORS)
- NON-Encrypting Ransomware (LOCKER)
- LEAKWARE (DOXWARE)
ENCRYPTING RANSOMWARE (ENCRYPTORS)
These are the type of Ransomware in which malware when injected into the system encrypts the data files and user names thus ransomware displays a message demanding a for the key to decrypt the data.The first Ransomware AIDS Trojan was a Encrypting Ransomware. Some of the known Encrypted Ransomware such as AIDS Trojan, Gpcode, TROJ.RANSOM.A, Archiveus, Krotten, Cryzip, and MayArchive, Cryptolocker,Wannacry have been rise on these occasion
NON-Encrypting Ransomware (LOCKER)
These are the types of Ransomware where the data or the files are not encrypted but the access of the system is restricted which makes the user to provide ransom to get the access of the system
Some of the known Non-Encrypting Ransomware are Winlock, Reverton
Leakware (Doxware)
These are the types of ransomware where an attacker after injecting the trojan and getting the access of an user threatens to publish stolen information from the victim’s computer system rather than deny the victim access to it.
Ransomware Characteristics
- It features unbreakable encryption, which means that you can’t decrypt the files on your own (there are various decryption tools released by cyber security researchers – more on that later)
- It has the ability to encrypt all kinds of files, from documents to pictures, videos, audio files and other things you may have on your PC.
- It can scramble your file names, so you can’t know which data was affected. This is one of the social engineering tricks used to confuse and coerce victims into paying the ransom.
- It will add a different extension to your files, to sometimes signal a specific type of ransomware strain.
- It will display an image or a message that lets you know your data has been encrypted and that you have to pay a specific sum of money to get it back.
- It requests payment in Bitcoins, because this crypto-currency cannot be tracked by cyber security researchers or law enforcements agencies.
- Usually, the ransom payments have a time-limit, to add another level of psychological constraint to this extortion scheme. Going over the deadline typically means that the ransom will increase, but it can also mean that the data will be destroyed and lost forever.
- It uses a complex set of evasion techniques to go undetected by traditional antivirus (more on this in the “Why ransomware often goes undetected by antivirus” section).
- It often recruits the infected PCs into botnets, so cyber criminals can expand their infrastructure and fuel future attacks
- It can spread to other PCs connected in a local network, creating further damage
- It frequently features data exfiltration capabilities, which means that ransomware can extract data from the affected computer (usernames, passwords, email addresses, etc.) and send it to a server controlled by cyber criminals
History of Ransomware
It may be difficult to imagine, but the first ransomware in history emerged in 1989 (that’s 27 years ago). It was called the AIDS Trojan, whose modus operandi seems crude nowadays. It spread via floppy disks and involved sending $189 to a post office box in Panama to pay the ransom.
How times have changed!
The appearance of Bitcoin, and evolution of encryption algorithms helped turn ransomware from a minor threat used in cyber vandalism, to a full-fledged money-making machine. As a result, every cybercriminal wants to be a part of this.
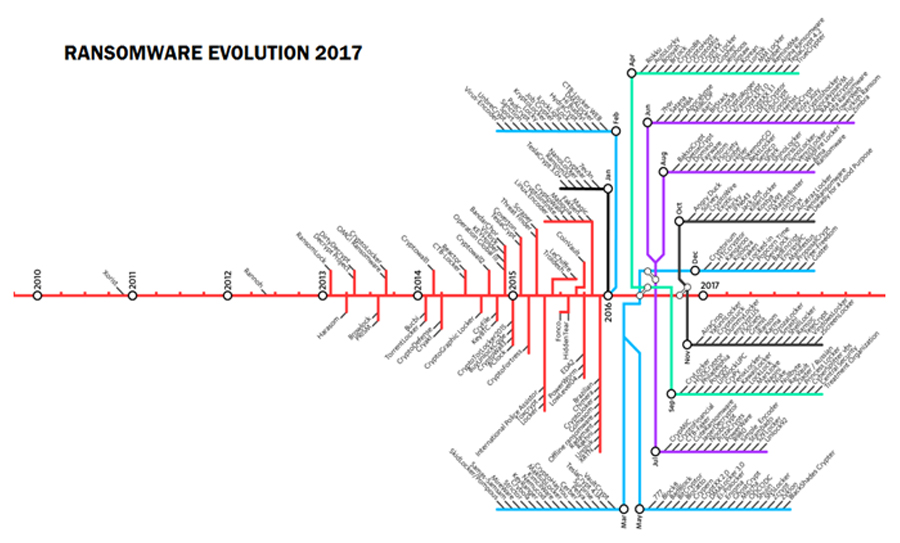
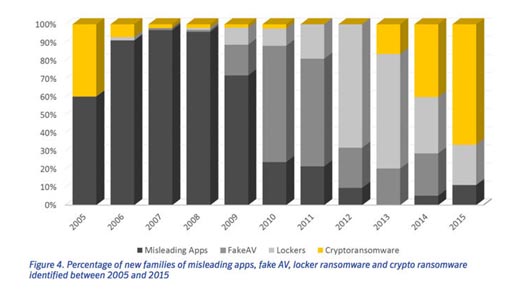
This graph shows just how many types of encrypting malware researchers have discovered in the past 10 years
Statistical data of Different Ransomware that has been evolved with in a decade which you can see in the figure
Ransomware Targets
- Cybercriminals targets companies and organizations which are far more profitable than users,
- Some departments like Ministry Departments, police departments, city councils and even schools andhospitals.
- Cyber criminals target various types of Internet users. This may help you better understand why things happen as they do right now.
Ransomware Transfusion
Ransomware is one of the Important malware that need to be provided more importance. Few ways the ransomware can be transfused or transmitted
- Spam email campaigns that contain malicious links or attachments (there are plenty of forms that malware can use for disguiseon the web);
- Security exploits in vulnerable software;
- Internet traffic redirects to malicious websites;
- Legitimate websites that have malicious code injected in their web pages;
- Drive-by downloads;
- Malvertising campaigns;
- SMS messages (when targeting mobile devices);
- Botnets;
- Self-propagation (spreading from one infected computer to another); WannaCry, for instance, used an exploit kit that scanned a user’s PC, looking for a certain vulnerability, and then launched a ransomware attack that targeted it.
- Affiliate schemes in ransomware-as-a-service. Basically, the developer behind the ransomware earns a cut of the profits each time a user pays the ransom.
How Ransomware are hidden from Antivirus?
- Ransomware signatures are not updated in Antivirus Database
- Malware Security Researcher are less aware about malware prevention
- Encrypted Network traffic makes much difficult to detect
- Anti sand Box Mechanics
- Fast Flux – the DNS send from attackers are numerous thus it is hard to find by virus
- Encrypted Payloads
- Polymorphic behavior
Protection is better than cure
- Backup Data regularly
- Configure your mail server by Anti-spam setting
- Suspicious Mails – Think before opening a mail
- Avoid Suspicious Link – check URL before going through it
- Patch and update Operating System regularly
- Turn on Firewall
- Regular Security Auditing in Organization
- Disable macros and ActiveX for piracy version software
- Implement strong Password
- Implement application whitelisting on your endpoints to block all unknown and unwanted applications
Tactical Solution Approach for Ransomware
Find available decryption tools. – A wealth of free decryption tools that can detect and remove screen-locker ransomware and certain variants of crypto-ransomware are now readily available from different security vendors. These can be used to avoid having to pay for corresponding decryption keys.
Implement a comprehensive data backup and recovery plan – Developing a comprehensive backup and recovery plan ensures that an organization’s valuable data is intact even after cases of data loss, which isn’t limited to ransomware infections. With this in place, the organization will be able to easily get back on its feet and resume operations.
Conduct post-incident analysis of the infection – Once the incident has been properly dealt with, investigate and scope the breadth and magnitude of the infection. More importantly, analyze the source of the infection to identify vulnerabilities and system weaknesses that should be addressed to prevent recurrence.
A sandbox analysis of the ransomware in question could help determine the malware’s behavior. This could also be used to identify Indicators of Compromise from its capabilities, routines, and tactics employed that would improve detection and develop ways to prevent future incidents.
The rapid development of ransomware with updated variants and families introduced almost daily shows that cybercriminals see this as a lucrative form of attack. A multi-layered approach to security is vital in ensuring that all possible entry points are well-defended from ransomware.
Author: Arul Selvar | Posted On: 25th May 2017 | Category: Article







